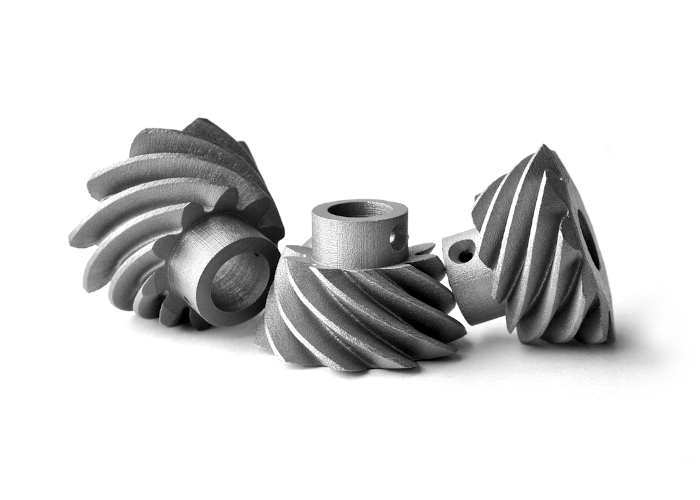
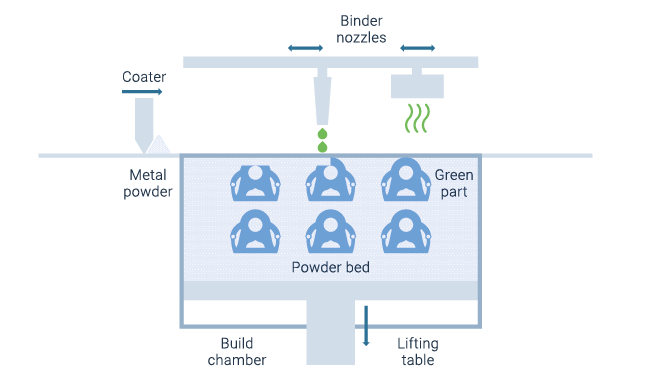
Binder Jetting is especially suited for small part sizes in the range between 5 to 50 mm. Due to the debinding and sintering process and the current state of knowledge, thinner wall thicknesses are preferred. With a surface roughness of about Ra of 5 µm, surface quality is high compared to other metal Additive Manufacturing technologies.
Since the bonding between the polymer ink and metal powder during the 3D printing process takes place without the melting of the metal component, no dimensional distortions occur due to thermal effects. Additionally, the surrounding powder bed supports overhangs and complex geometries. Therefore, no additional support structures are required for the printing process. The dimensional accuracy of printed green bodies is very high.
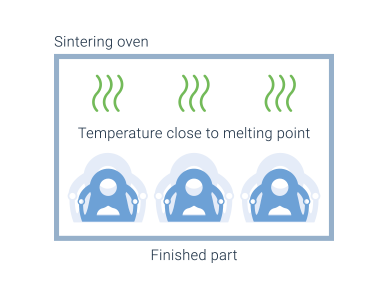
However, the elevated temperatures and shrinkage during the sintering process require deep knowledge on process specific design. Poorly designed or insufficiently supported green bodies show large distortion and cracking during the sinter process. The shrinkage can be around 20% per direction. While the green body printing process does not require supports, such stabilizing structures are sometimes required for the sintering to avoid undesired deformation.
It is expected that Binder Jetting will replace low volume, high cost metal injection molding parts. These parts typically have applications in automotive, medical or tooling industry. Low volume jewelry and consumer goods are also potential applications for BJT.